Circular Economy
- Home
- /
- Circular Economy
Circular Economy by CSX
Worldwide more raw materials are used than the earth can manage. In addition, ‘the leaks’ in the system cause emissions to soil, water and air, a heavy burden to our environment. Finally, emissions of greenhouse gases as a result of the use of (fossil) raw materials cause global warming.
Drastically reducing the consumption of raw materials and replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources are necessary to keep the earth livable and our economy running. Keywords are: circular, resource efficiency and climate neutral.
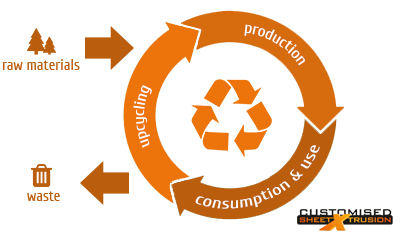
A circular economy is characterized by:
Preventing and limiting the use of primary raw materials in the production of materials, goods and foodstuffs.
Keep materials and goods in a cycle for as long as possible: closing chains.
Prevent the generation of waste and emissions as much as possible. Cycles in the circular economy.
A circular economy is characterized by:
A grey, technical cycle in which metals, fossil raw materials and minerals remain in the cycle for as long as possible.
A biological cycle that provides our future CO2-neutral and circular economy with renewable raw materials from living nature.
Bio-raw materials (crops, trees, algae, plants, animal residues) are used as a necessary and valuable raw material for: chemistry, construction, agriculture and manufacturing.

